In recent years, particularly with the explosive growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, a new concept has been creating a significant buzz across global Learning & Development (L&D) forums and conferences: the “Learning Stack of the Future“ This concept is not merely a fashionable term; it represents a fundamental shift in how organizations build and deliver continuous, personalized learning experiences for their employees in a volatile world.
Many L&D professionals in Vietnam might perceive this concept as distant, seemingly reserved for multinational corporations with enormous training budgets, vast tech teams, and limitless experimental capacities. However, reality proves that, whether intentionally or not, a significant number of Vietnamese businesses have already begun to embrace this trend, albeit on a smaller scale or through initial pilot projects. The greatest challenge lies not in owning complex systems, but in deeply understanding the core essence of the “Learning Stack of the Future” and, more importantly, how to apply AI intelligently and practically, even when starting from scratch or with an extremely limited budget.
1. Demystifying the “Learning Stack of the Future” – The Foundation for an Era of Continuous Learning
To understand how AI integrates and shapes the future of learning, we must first grasp the concept of the “Learning Stack of the Future” – a new mindset for the corporate learning ecosystem.
1.1. Context of Emergence and Strategic Importance
The “Learning Stack of the Future” is not a sudden invention but rather the result of an evolution in human learning and development thinking. It reflects a shift from “event-based learning” (e.g., periodic courses) to “continuous learning” and “learning in the flow of work.” Factors driving the emergence of this concept include:
- Rapid pace of technological and business change: Creating a continuous need for learning to adapt and innovate.
- Skill shortages: Businesses need to develop internal talent to bridge skill gaps.
- Learner’s desire for personalization: The new generation of employees demands learning experiences tailored to their individual needs and styles.
- Technological advancements: Especially AI, Big Data, and flexible learning platforms.
Leading research and consulting organizations like Deloitte, in their “Global Human Capital Trends” reports, consistently emphasize the evolving learning paradigm, from learning “for work” to learning “in work” and learning “as work.” Josh Bersin, a reputable analyst in HR and L&D, also frequently refers to the “learning ecosystem” as an integrated system of diverse learning resources, with the “Learning Stack” forming a structural part of it. (Sources: Josh Bersin, “The Learning Ecosystem: A New Strategy for Learning and Development,” Deloitte’s Human Capital Trends reports).
The importance of building a “Learning Stack of the Future” lies in its ability to:
- Optimize performance: By providing knowledge and skills at the right time and place, helping employees solve problems and make decisions faster.
- Enhance competitiveness: Building a workforce capable of adapting, innovating, and outperforming competitors.
- Increase employee engagement: When employees feel invested in their personal and professional development.
- Control costs effectively: Leveraging technology to scale learning without linearly increasing expenses.
- Position L&D as a strategic partner: Shifting L&D from a supporting role to a direct creator of business value.
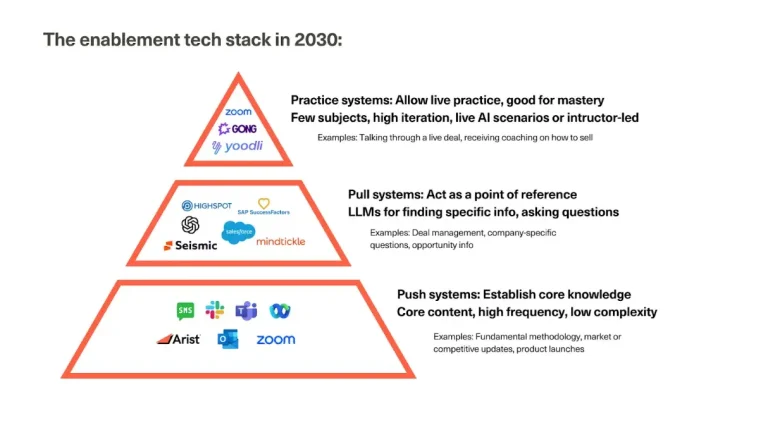
1.2. The Three Layers of the “Learning Stack of the Future” and Their Strategic Significance in L&D
The modern “Learning Stack” is built with three interacting and complementary layers, each representing a different approach to learning. Interestingly, AI now plays a central role, acting as a “binding agent” and “catalyst” to optimize effectiveness across all three layers.
1.2.1. Layer 1: Push Learning – Intelligent and Personalized Content Delivery (Personalized Push)
- Definition: This is a form of learning where content is actively “pushed” to learners by the organization. Traditional examples include mandatory compliance training, instructional videos, internal newsletters, email announcements about new policies/procedures, or scheduled microlearning programs.
- Limitations of Traditional Push: The biggest problem with traditional Push Learning is its “one-way” nature and lack of personalization. Everyone receives the same content at the same time, regardless of their differing needs, roles, or proficiency levels. This leads to low engagement and adoption rates, content being easily ignored, wasted resources, and reduced communication effectiveness.
- Strategic Significance in Modern L&D: In the “Learning Stack of the Future,” Push Learning is upgraded to Personalized Push. The core meaning shifts from merely “sending it out” to “sending the right content, at the right time, in the right format, to the right person.” AI helps analyze individual roles, needs, learning habits, and interaction history to select the most suitable delivery method, from content and timing to format (e.g., short videos, infographics, podcasts, summarized documents). The goal is to maximize content adoption and interaction, ensuring important messages are conveyed most effectively to each individual, reducing information overload, and increasing content relevance.
1.2.2. Layer 2: Pull Learning – On-Demand and Immediate Information Retrieval (On-demand Pull)
- Definition: This is a form of learning where learners actively “pull” information, seeking answers or resources when a need arises during their work process or when they encounter an immediate problem. This can include searching internal databases, asking colleagues, consulting knowledge platforms, or searching on the internet.
- Limitations of Traditional Pull: In previous learning approaches, the process of “learning something and then having to re-find materials or ask colleagues” was often time-consuming, laborious, and frustrating. Information could be scattered, difficult to find, outdated, or inconsistent. Waiting for responses from colleagues or experts also slowed down work progress.
- Strategic Significance in Modern L&D: Pull Learning in the “Learning Stack of the Future” emphasizes the ability to access information quickly, accurately, and immediately at the point of need (just-in-time learning). This layer transforms the knowledge search process into a seamless experience, positioning L&D as an “internal learning assistant” or the “company’s own Google.” The objective is to minimize work interruptions, empower employees to self-serve, solve problems, and make effective decisions directly within their workflow, thereby enhancing overall organizational productivity.
1.2.3. Layer 3: Practice – Transforming Knowledge into Skills and Behavior (Experiential Practice & Application)
- Definition: This learning layer focuses on applying knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios through practical activities, simulations, experimentation, role-playing, and receiving feedback. This is the most critical stage for transforming knowledge from “knowing” to “being able to do” and “doing well.”
- Limitations of Traditional Practice: Learning without sufficient opportunities for practice or timely feedback easily leads to forgetting and the inability to form skills. Traditional practice methods were often limited in scale and costly (e.g., requiring one-on-one expert guidance, physical space for complex simulations), or lacked personalized feedback.
- Strategic Significance in Modern L&D: Practice is where knowledge truly becomes a skill and is ingrained in an employee’s subconscious. In the “Learning Stack of the Future,” this layer is enhanced to provide rich, safe, highly customizable, and immediate feedback-driven practice opportunities. The goal is to help employees practice in a low-risk environment, experiment with complex scenarios, receive immediate feedback, and iterate until skills are mastered and become natural behaviors in their work, directly improving job performance and employee confidence.
These three layers do not exist in isolation but interact and complement each other, forming a comprehensive, flexible learning ecosystem. AI plays a powerful catalytic role, optimizing and personalizing the experience at each layer, transforming theory into action, and knowledge into tangible results.
2. AI – A Powerful “Catalyst” for the “Learning Stack of the Future” (Even on a Limited Budget)
Now that we have a clear understanding of the three layers of the Learning Stack, we will delve into how AI, particularly accessible LLMs and low-cost/free tools, can support each layer. The key is a mindset of leveraging these tools, not necessarily investing in expensive software.
2.1. AI Supporting Push Learning – Content Personalization is No Longer an “Enterprise Privilege”
The goal of modern Push Learning is personalization to ensure maximum content relevance and adoption. AI achieves this by analyzing (even limited) data about learners and adapting content and delivery methods.
- Creating Diverse Content and Personalized Summaries:
- Practical AI Application: Instead of sending a long document and hoping employees read it all, you can use ChatGPT/Gemini to:
- Summarize documents, reports, and lectures: Ask AI to summarize a long text, a YouTube video, into bullet points, mind maps, or a concise, easy-to-understand paragraph. You can paste YouTube links or copy/paste content directly.
- Personalize by role/need: For example, if you have a “New Company Code of Conduct.” Ask AI: “Summarize this document, focusing on what Sales employees most need to know about customer interactions.” Then: “Provide a similar summary but focusing on data security aspects for the IT team.” AI will generate different versions of the summary, tailored to each audience.
- Transform formats: Convert a block of text into a microlearning video script, an infographic text, or interactive quiz questions for quick knowledge checks.
- Specific Tools: ChatGPT (the free version is still incredibly powerful), Gemini (free version), Poe (allows access to and comparison of responses from various LLMs in one interface), online summarization tools like Summarize.tech (for YouTube videos), QuillBot (for text summarization and paraphrasing), and NotebookLM (for summarizing documents and generating content like podcasts from text).
- Practical AI Application: Instead of sending a long document and hoping employees read it all, you can use ChatGPT/Gemini to:
- Optimizing Delivery Time and Channel:
- Practical AI Application: While AI doesn’t directly send emails or manage distribution systems, it can analyze historical data (if available, e.g., from previous email marketing campaigns) on email open rates and click-through rates for different target groups. This helps it suggest optimal sending times or preferred content formats. You can input data into AI and ask for trend analysis.
- Specific Tools: Basic email marketing platforms like Mailchimp (with basic analytics and A/B testing features), or manual analysis with Excel after using AI to synthesize insights from raw data.
- Real-world Example (Retail Company A):
- Situation: The company was launching a new sales campaign with many complex products and promotional programs. Sales employees were often overwhelmed with information and struggled to grasp everything.
- L&D Solution with AI: The L&D team used ChatGPT to:
- Summarize the key highlights of each product and benefits for target customers into concise bullet points.
- Transform detailed promotional information into “quick answers” for frequently asked customer questions.
- Create “mini-scripts” for sales employees when advising on new products.
- All content was packaged into microlearning newsletters sent via Zalo or internal apps at the beginning of each week, personalized for each product group the employee was responsible for.
- Result: Employees grasped information faster, felt more confident in their consulting, and the number of queries about products/programs significantly decreased.
2.2. AI Supporting Pull Learning – An Accurate and Instant “Internal Google”
The goal of Pull Learning is the ability to access information quickly, accurately, and at the precise moment of need. AI can transform internal knowledge repositories into dynamic, easily searchable, and responsive resources.
- Building Basic Learning/Knowledge Support Chatbots:
- Practical AI Application: This is one of the highest ROI AI applications for Pull Learning.
- Create a Knowledge Base: Consolidate all important company documents (Standard Operating Procedures – SOPs, software user guides, HR FAQs, sales policies, product information, lessons learned from projects). This is the most labor-intensive but critical step.
- Train AI (Fine-tuning or Retrieval Augmented Generation – RAG): For AI to answer questions about internal documents, you need to “train” it. With a limited budget, you don’t need to build your own AI model. Instead:
- Use LLM APIs: Services like OpenAI API (for ChatGPT) or Google AI Studio (for Gemini) allow you to send questions and provide context (your documents) for AI to answer.
- No-code/Low-code tools: Many platforms help you create LLM-integrated chatbots and “feed” them your data without coding (e.g., Google Dialogflow Essentials (with free/trial versions), CustomGPT, Botpress (community edition), Zapier/Make to connect Google Sheets/Docs with LLMs).
- Use AI as a Contextual Search Tool: If building a chatbot is too complex, employees can simply copy a section of an internal document (or paste multiple document snippets) into ChatGPT/Gemini and ask: “Explain this passage,” “Summarize the steps in Process X,” “Find information Y in these documents,” “Compare Policy A and Policy B.” AI will help them quickly extract the necessary information.
- Specific Tools: Google Dialogflow Essentials, CustomGPT, Botpress, Zapier, Make, OpenAI/Google API services.
- Practical AI Application: This is one of the highest ROI AI applications for Pull Learning.
- Generating Automated and Instant Answers:
- Practical AI Application: AI can help generate answers to frequently asked questions about operational procedures, HR policies, product information, or basic technical issues. This significantly reduces the burden on support teams (HR, IT, Sales Ops) and empowers employees to self-serve, resolving problems faster.
- Example: Instead of calling HR to ask about the leave registration process, an employee can query the chatbot and receive step-by-step instructions and the correct form link.
- Real-world Example (IT Services Company B):
- Situation: The company had hundreds of projects, each with its own documentation, processes, and lessons learned. Employees often spent a lot of time searching for information when switching projects or needing to resolve issues.
- L&D Solution with AI:
- The L&D team collaborated with IT to compile all project documents (procedures, reports, bug logs, solutions) into a centralized repository (e.g., Google Drive or SharePoint).
- They used an LLM-integrated chatbot tool (e.g., a simple chatbot built on Google Dialogflow or using the OpenAI API) and “fed” it data from the repository.
- When an employee needed information about a specific bug in an old project, they simply typed the question into the chatbot. The chatbot would search and provide the most relevant solution snippet or extract information from reports.
- Result: Employee information search time decreased by 50%, significantly boosting productivity, especially when dealing with complex issues or new projects.
2.3. AI Supporting Practice – Unlimited Practice Environments for Skill Development
Practice is where knowledge transforms into skills. AI can create safe, flexible, and personalized practice environments that far surpass traditional methods.
- Creating Dynamic Simulation/Role-play Scenarios:
- Practical AI Application: This is one of the most innovative and valuable applications of AI in Practice.
- Designing Diverse Scenarios: Ask ChatGPT/Gemini to create detailed role-play scenarios for specific skills (e.g., “Create 5 role-play scenarios for Sales employees to practice handling customer objections regarding Product X pricing, with increasing difficulty,” “Create a difficult communication scenario with a challenging colleague, requiring conflict resolution,” “Create a mock interview scenario for a Marketing Executive position”).
- Interactive Role-play (Conversational AI Role-play): You (the learner) can ask ChatGPT/Gemini: “Act as a difficult customer complaining about Product A quality. I will practice my complaint handling skills. Please react like a real customer and create unexpected situations.” AI will respond as a realistic character, helping the learner practice and develop diverse responses, thereby honing soft skills and adaptability.
- Multilingual Practice: If you want to practice speaking English/Japanese/Korean, AI can act as a native speaker and respond in that language.
- Specific Tools: ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude (powerful LLMs), or simple AI-integrated scenario/simulation platforms (e.g., Virbela for VR/AR environments if budget allows, but initially, LLMs are sufficient).
- Practical AI Application: This is one of the most innovative and valuable applications of AI in Practice.
- Generating Automated Feedback and Detailed Assessment Checklists:
- Practical AI Application: After the learner practices (e.g., records a role-play, or copies/pastes the chat transcript with AI into another window), AI can be used to:
- Analyze and Suggest Feedback: Paste the conversation transcript into AI and ask: “Analyze this dialogue, identify strengths and weaknesses in the speaker’s listening/communication/persuasion skills. Provide specific suggestions for improvement and better alternative phrases.”
- Create Customizable Assessment Checklists: Ask AI to “Create a checklist for evaluating effective presentation skills with specific criteria (speech structure, tone of voice, body language, audience interaction) and clear scoring rubrics.” Learners can then self-assess or ask colleagues to evaluate them based on this checklist.
- Specific Tools: ChatGPT, Gemini, speech-to-text AI tools (e.g., Google’s Speech-to-text AI, Speechnotes).
- Practical AI Application: After the learner practices (e.g., records a role-play, or copies/pastes the chat transcript with AI into another window), AI can be used to:
- Real-world Example (Bank C – Teller Training):
- Situation: New tellers needed to practice complex product advisory skills and handle difficult customer situations without affecting actual customer experience.
- L&D Solution with AI:
- The L&D team designed dozens of simulated communication scenarios (customer complaints, customers wanting to cancel services, customers requesting impossible products).
- Tellers used ChatGPT for practice. They asked ChatGPT to role-play as a customer in each scenario. After each practice session, they pasted the conversation transcript into ChatGPT and asked for analysis of their language, demeanor, professionalism, and suggestions for improvement.
- Result: Tellers gained significant confidence in handling difficult situations, their complaint resolution abilities improved, and the time required for on-the-job training at the counter was reduced. The cost of practice was virtually zero.
3. Practical Roadmap: Implementing AI in L&D with Zero (or Very Low) Budget – Solid Steps Forward
Implementing AI doesn’t necessarily require a large, expensive project. You can start with small, practical steps and gradually scale up.
3.1. Step 1: Identify Your Biggest L&D “Pain Point” (5-7 days)
- Problem-Solving Mindset: Don’t jump straight into AI. First, look at your current L&D processes. What is the biggest bottleneck, causing wasted time, resources, or inefficiency?
- Is the L&D team too busy drafting basic documents and content? (Push)
- Do employees struggle to find essential information for their daily work? (Pull)
- Do employees complete courses but have few opportunities to practice, leading to knowledge decay? (Practice)
- Is it difficult to collect high-quality feedback after practice sessions? (Practice)
- Is your budget limited for soft skills courses or one-on-one coaching?
- Choose 1-2 Specific, High-Priority Problems: Focus on one or two issues that you believe AI can significantly address, and these are the most “painful” problems for both L&D and employees.
3.2. Step 2: Select Suitable AI Tools and Learn Basic Usage (3-5 days)
- Start with Free and Accessible Options:
- ChatGPT (free version): An excellent choice for content generation, summarization, scripting, and role-playing tasks.
- Gemini (free version): Similar to ChatGPT; try both to compare and find the tool that best suits your workflow.
- Poe.com: A useful platform that allows you to access and compare responses from multiple free LLMs within a single interface.
- Online Video/Text Summarization Tools: E.g., Summarize.tech (for YouTube summaries), QuillBot (for text paraphrasing and summarization).
- Learn Basic Prompt Engineering: This is the most crucial skill for unlocking the power of LLMs. Numerous free courses, articles, and video tutorials on “Basic Prompt Engineering” are available on YouTube, Coursera, or tech blogs. Focus on principles like: clarity, specificity, providing context, and requesting output format.
3.3. Step 3: Conduct a Small Pilot (2-4 weeks)
- Select a Small Group/Specific Department: Do not try to implement across the entire company immediately. Choose a small group that is forward-thinking and willing to experiment.
- Execute a Small, Focused Experiment on Your Chosen Problem:
- Example (Push): If the problem is overlooked new information. Use AI to create 3 versions of a new policy announcement (concise summary, infographic text, Q&A) for one department. Send these versions and measure open/interaction rates.
- Example (Pull): If the problem is employees wasting time searching for procedures. Select 5 frequently asked-about procedures. Use AI to generate concise, standardized answers. Guide a small group of employees to use AI (e.g., ChatGPT) to ask questions about these 5 procedures. Collect feedback on usefulness and search time.
- Example (Practice): If the problem is a lack of opportunities for presentation skills practice. Design 3 difficult presentation scenario scripts. Guide a small group of employees to use AI to role-play as a difficult audience/boss for practice. Collect feedback on the practice experience and self-reported confidence improvement.
- Collect Qualitative and Quantitative Data and Feedback: Even in a pilot, record what works well, what needs improvement, and user reactions. Google Forms can be used for quick surveys.
3.4. Step 4: Evaluate, Learn, and Scale (Continuous)
- Analyze Pilot Results: Did AI actually help solve the chosen “pain point”? Was it more effective than the old method? Calculate ROI (if possible, even if it’s non-financial ROI like time saved or increased satisfaction).
- Adjust and Refine: Based on feedback and results, fine-tune your AI usage, modify prompts, or experiment with other tools/methods.
- Gradual Scaling: Once you have experience and see clear (even small) effectiveness, gradually expand the scope of AI application to other programs, departments, or upgrade tools if the budget allows.
- Internal Training and Knowledge Sharing: Organize small workshops, share your company’s successful case studies with the L&D team and managers. Encourage them to participate in experimentation and discover new AI applications. Build a community of L&D pioneers.
4. Potential Challenges and Future Direction – Leading the Way, Not Being Left Behind
While AI offers numerous opportunities to revolutionize L&D, implementation comes with certain challenges. Proactively identifying and planning for these will help organizations overcome barriers.
4.1. Challenges to Address
- Budget and Technology: Although starting with low costs is possible, deeper AI integration into existing L&D systems (e.g., LMS, HRIS) requires significant investment. Organizations need to weigh benefits against costs.
- L&D Team Skills: This is a major hurdle. Traditional L&D teams might lack skills in IT, data analytics, or especially Prompt Engineering for effective AI interaction. A plan for reskilling or hiring new talent is necessary.
- AI Quality and Accuracy: LLMs can sometimes generate “hallucinations” (inaccurate or fabricated information) or lack sufficient depth or human nuance. AI-generated content needs rigorous human review, especially for critical or sensitive information.
- Data Security and Privacy: When using AI to process employee data or proprietary company information, security and privacy become paramount. Organizations need clear policies on AI usage, avoiding sharing sensitive information with public AI models. Explore secure AI solutions (on-premise or Private Cloud) if budget allows.
- Learning Culture and Resistance to Change: Not all employees will be ready to adapt to new AI-powered learning methods. Some might feel anxious about technology replacing human roles, or simply be uncomfortable with changing habits. Clear, transparent communication strategies and a culture of experimentation and learning from mistakes are essential.
4.2. Future Direction and Long-Term Vision – Making AI a Strategic Ally
AI is not a solution to replace humans; it’s a tool to elevate the role of L&D and individual employees.
- AI doesn’t replace L&D, it elevates L&D: AI will automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks like basic content creation, report generation, and FAQ answering. This frees up the L&D team to focus on higher-value activities: strategizing L&D, designing complex learning experiences, deep data analysis for valuable insights, and building relationships, coaching people. L&D professionals will become “learning experience architects” and “capability strategists.”
- Early adoption is a competitive advantage: This trend won’t wait. Starting early, even with small steps, helps the organization and L&D team become familiar, understand, adapt quickly, and accumulate experience. Pioneers will have a significant advantage in optimizing talent and adapting to the future of work.
- Connecting People and Technology: AI is a tool. The most meaningful learning experiences still require human guidance, empathy, and feedback. L&D needs to balance leveraging AI to optimize processes with maintaining the human element in coaching, mentorship, and building learning communities.
- Agile Mindset, Experimentation, and Continuous Learning: There’s no need to rush into building a multi-million dollar “stack of the future” immediately. Just Push at the right time, Pull at the right place, Practice in the right way, and let AI support gradually, one piece at a time, at the pace and needs of your organization. Failure in experimentation is part of the learning process.
- Measure Effectiveness: Don’t forget to measure the effectiveness of AI initiatives in L&D. Utilize the Kirkpatrick 4-level model (as mentioned previously) to assess AI’s impact at each level: from learner reaction, to what they learned, how their behavior changed, and finally, the impact on business results. This will help you demonstrate ROI and gain support for future projects.
Making AI an L&D Ally – Building the Future of Learning Today
The “Learning Stack of the Future” with AI support is no longer a luxury or a distant concept. It is the inevitable future of L&D, where learning becomes more personalized, flexible, and efficient than ever before. For businesses in Vietnam, the challenge is not in immediately acquiring expensive technologies, but in proactive action, an experimental mindset, and the ability to leverage the most accessible AI tools to solve real-world problems.
Start today by identifying a specific problem, choosing a free or low-cost AI tool, launching a small pilot, and most importantly, continuously learning, measuring, and adapting. AI is not a “giant” exclusively for large corporations; it is a powerful assistant that every L&D team, with creativity and strategic thinking, can leverage.
And if you are seeking a structured roadmap, a practical program to master these concepts – from designing training programs with clear outcomes, applying new technologies, to measuring effectiveness with real KPIs and ROI – then the NextGen L&D program by HRDC is a highly recommended choice. This program not only equips you with knowledge of advanced learning models but also provides concrete tools and methodologies to confidently implement and manage your own “Learning Stack,” transforming seemingly complex concepts into tangible actions that create sustainable value for your business.
Begin your journey to build the future of L&D today!
Related Articles:
- The Future of Work: What L&D Needs to Prepare for Rapid Changes
- L&D Competency Development Skills Course – HRDC
- 4 Things You Need to Know About the R.O.I. Model in Evaluating Training Effectiveness
- L&D Challenges in the Digital Age – 2025
HRDC – Learn – Apply – Succeed
📌LTG: https://www.learntogrow.com.vn/nextgen-l_d
🌐Website: https://hrdc.com.vn
🚨Hotline: 0866 566 366 – 0585 27 28 29
📧Email: chamsockhachhang@hrdc.com.vn
🏬Address: Dolphin Plaza – 28 Tran Binh – My Dinh 2 Ward – Nam Tu Liem District – Hanoi